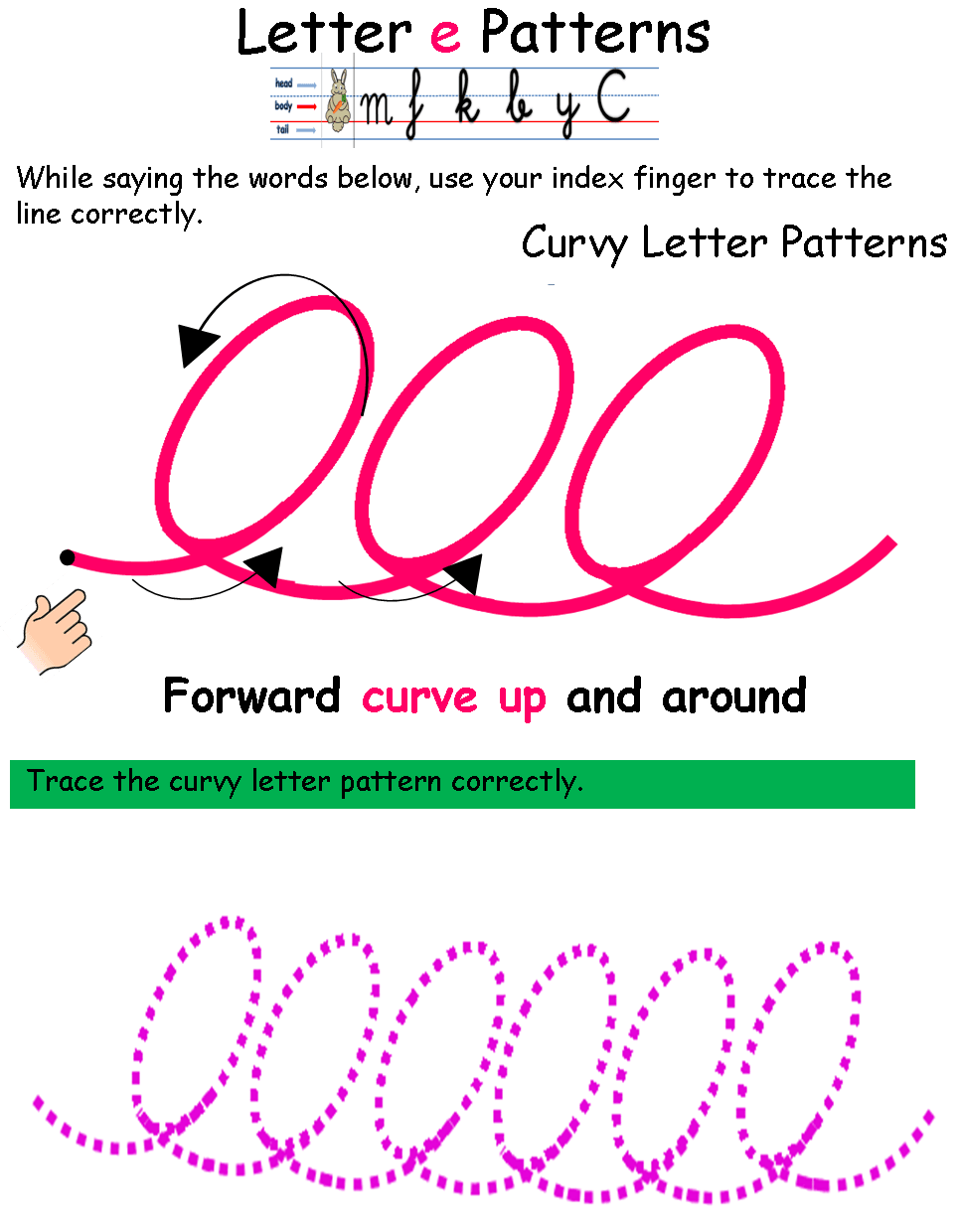
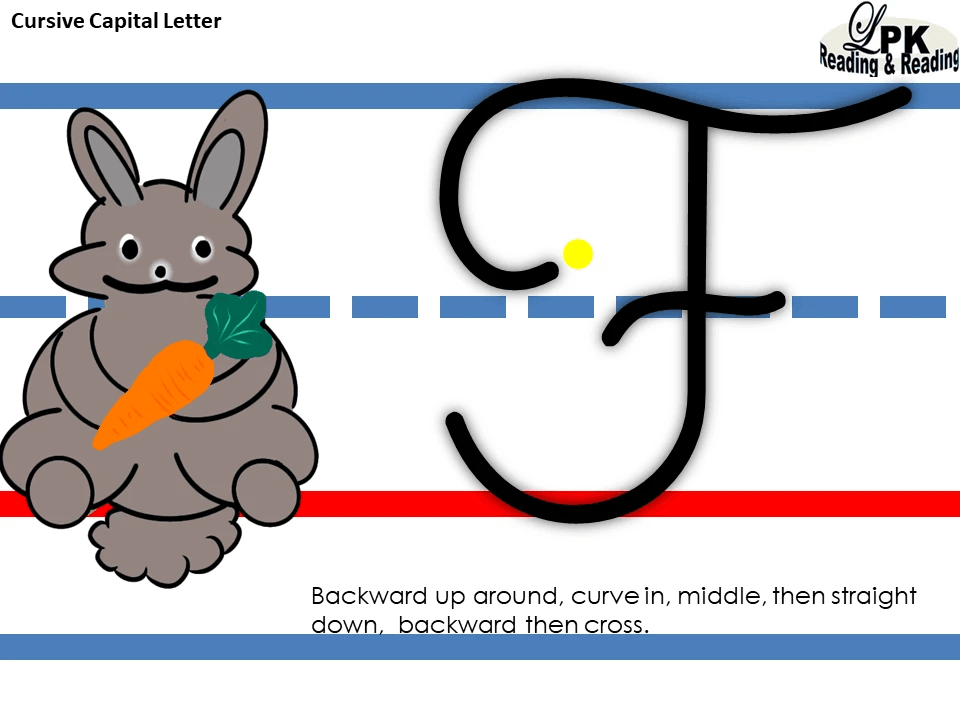
Learning cursive letter formation with spatial awareness offers a multitude of benefits for children aged 7 and above.


1. Enhanced Fine Motor Skills: Practicing cursive letter formation with spatial awareness involves intricate hand movements, improving fine motor skills in children.
2. Flow and Continuity: Spatial awareness helps kids understand the flowing connections between cursive letters and words, leading to smoother and more continuous writing.
3. Improved Spatial Reasoning: Learning cursive with spatial awareness enhances children's spatial reasoning abilities, contributing to better overall spatial awareness and cognitive development.
4. Sense of Accomplishment: As kids master cursive penmanship, they experience a sense of achievement and pride, boosting their self-esteem and confidence.
5. Better Legibility: Spatial awarenessfosters a deeper understanding of letter structure and spacing, resulting in neater and more legible cursive writing.
6. Efficiency in Writing: With spatially guided cursive writing, children can focus more on the content of their writing and less on the mechanics, leading to increased writing efficiency.
7. Fluency and Clarity: As kids become more confident in cursive, they can express their ideas with greater fluency and clarity, promoting effective communication.
8. Improved Productivity: Increased writing speed and legibility through spatial awareness lead to improved productivity in completing written assignments.
9. Self-Expression: With improved cursive penmanship, children can express themselves more authentically and
creatively in their writing.
10. Independence in Communication: The ability to write in cursive empowers children to communicate effectively and independently, both in academic and personal settings.
11. Appreciation for Writing: Spatial awareness in cursive instruction makes writing a more enjoyable and fulfilling activity, encouraging a positive attitude towards writing.
12. Transferable Skills: Spatial awareness skills developed in cursive writing can be applied to other areas, such as art, design, and problem-solving.
The personal independence and confidence cultivated through cursive penmanship extend well beyond writing. As kids become more proficient in cursive, they experience a sense of accomplishment that bolsters their self-esteem (Puranik & Lonigan, 2014).
With spatial awareness, children develop a deeper understanding of letter
structure and spacing, resulting in improved legibility and neater presentation of their written work (Graham et al., 2016). As they compose notes, letters, or assignments in cursive, the natural flow of the writing process is enhanced, enabling students to focus more on the content and less on the mechanics of forming each letter.
This new found efficiency contributes to increased productivity, enabling children to express their ideas with greater fluency and clarity (Berninger et al., 2017). Ultimately, the ability to write cursive with confidence empowers children to communicate effectively and express themselves more authentically in both academic and personal settings, encouraging a strong sense of independence and self-assurance.
By incorporating spatial awareness into cursive letter formation, educators provide a well-rounded learning experience that not only enhances children's writing abilities but also nurtures their personal growth, independence, and self-assurance in various aspects of life.
The Penmanship Line Design of Both Peppy the Puppy and Alf The Rabbit Rationle
The innovative penmanship line design, with the tail line being shorter than the head and body lines, promotes efficient writing skills development in students. Here are theoretical reasons supporting this
methodology:
1. Motor Skill Development: The shorter tail line encourages fluid movement and faster transitions between letters, fostering improved motor skills and handwriting speed.
2. Letter Formation: By reducing the tail line's length, students focus on the critical elements of letter formation (head and body) and quickly move to the next letter, promoting better letter connections.
3. Muscle Memory: This design helps develop muscle memory for letter writing, as students learn to efficiently transition between letters without unnecessary extension.
4. Readiness for Regular Lines: Gradually introducing students to varying line heights prepares them for writing on standard adult lines, easing the transition.
5. Enhanced Legibility: Faster writing speeds and smoother transitions contribute to improved handwriting legibility.
6. Reduced Fatigue: Shorter tail lines minimize unnecessary movement, reducing hand fatigue and promoting longer writing sessions.
7. Better Pacing: This design encourages students to maintain a consistent writing pace, preventing slow and laborious writing.
8. Developmental Appropriateness: Tailoring line heights to students'
developmental needs supports optimal writing skill acquisition.
9.Kinesthetic Awareness: The varied line heights enhance kinesthetic awareness, helping students develop a sense of letter proportion and spacing.
10. Long-Term Efficiency: Mastering efficient handwriting techniques with this line design lays the foundation for future long writing proficiency.
Our penmanship line design effectively addresses the unique needs of developing writers, also children with special needs, and setting them up for success in handwriting and beyond.
References from professional theories supporting our Penmanship method:
Motor Skill Development
1.Occupational Therapy: The shorter tail line aligns with OT principles,
promoting efficient motor planning and execution (American Occupational Therapy Association, 2020).
2. Dynamic Temporal and Tactile Cueing: This method resonates with DTTTC, emphasizing fluid movement and timely transitions (Berninger & Amtmann,
2003).
Letter Formation and Muscle Memory
1. Handwriting Without Tears: The design mirrors HWT's emphasis on efficient letter formation and muscle memory development (Olsen, 2010).
2. Kinesthetic Learning: The varied line heights cater to kinesthetic
learners, reinforcing letter formation and motor skills (Hannafin & Hooper,
1995).
Readiness for Regular Lines and Legibility
1.Developmental Handwriting: This method aligns with DH's focus on gradual transitions to standard lines, promoting legibility (Benbow, 1995).
2. Handwriting Research: Studies show that efficient handwriting skills,
fostered by this design, contribute to better legibility (Berninger et al., 2012).
Reduced Fatigue and Better Pacing
1. Motor Control Theory: The shorter tail line reduces unnecessary movement, aligning with MCT's emphasis on energy-efficient motor control (Shumway-Cook & Woollacott, 2017).
2. Pacing and Fluency: This design promotes pacing and fluency, critical
components of handwriting proficiency (Alston & Taylor, 2017).
Developmental Appropriateness and Kinesthetic Awareness
1.Child Development Theories: The method respects children's unique
developmental needs, aligning with CD theories (Vygotsky, 1978).
2. Sensory Integration: The varied line heights enhance kinesthetic
awareness, supporting sensory integration principles (Ayres, 1972).
Frequently Asked Questions
The benefits of teaching cursive letter formation with spatial awareness:
1. Q: How does teaching cursive letterformation with spatial awareness improve fine motor skills in children?
A: Spatial awareness in cursive instruction involves intricate hand movements, which help develop and refine fine motor skills (James & Engelhardt, 2012).
2. Q: What role does spatial awarenessplay in enhancing the flow and continuity of cursive writing?
A: Spatial awareness helps children understand the graceful connections between cursive letters and words, resulting in smoother and more continuous writing (Graham & Santangelo, 2014).
3. Q: How does learning cursive with spatial awareness contribute to improved spatial reasoning abilities in children?
A: Spatial awareness in cursive instruction enhances spatial reasoning skills, promoting better overall spatial awareness and cognitive development (James & Engelhardt, 2012).
4. Q: Can teaching cursive letterformation with spatial awareness boost a child's self-esteem and confidence?
A: Yes, mastering cursive penmanship through spatial awareness encourages a sense of accomplishment and pride, positively impacting a child's self-esteem (Puranik Lonigan, 2014).
5. Q: In what ways does spatial awarenessin cursive writing lead to better legibility?
A: Spatial awareness helps children develop a deeper understanding of letter structure and spacing, resulting in neater and more legible cursive writing (Graham & Santangelo, 2014).
6. Q: Does learning cursive with spatialawareness improve writing efficiency for children aged 7 and up?
A: Yes, spatially guided cursive writing allows children to focus more on the content and less on the mechanics, leading to increased writing efficiency (Graham et al., 2016).
7. Q: How does spatial awareness incursive writing contribute to fluency and clarity in expression?
A: As children become more confident in cursive, they can express their ideas with greater fluency and clarity, promoting effective communication (Berninger et al., 2017).
8. Q: Can learning cursive with spatial awareness lead to improved productivity in completing written assignments?
A: Yes, increased writing speed and legibility achieved through spatial awareness contribute to improved productivity in written work (Graham & Santangelo, 2014).
9. Q: How does cursive writing with spatial awareness empower children's self-expression?
A: Mastering cursive penmanship allows children to express themselves more authentically and creatively in their writing (Berninger et al., 2017).
10. Q: Are the benefits of spatial awareness in cursive writing transferable to other areas of a child's life?
A: Yes, spatial awareness skills developed in cursive writing can be applied to other activities such as art, design, and problem-solving, enhancing overall cognitive abilities (James & Engelhardt, 2012).
References
· Berninger, V. W., Abbott, R.D., Jones, J., Wolf, B. J., Gould, L., Anderson-Youngstrom, M., ... & Apel, K. (2017). Early development of language by hand: Composing, reading, listening, and speaking connections; three letter-writing modes; and fast mapping in spelling. Developmental Neuropsychology, 42(5), 382-399. doi:10.1080/87565641.2017.1286228
· Graham, S., & Santangelo,T. (2014). Does spelling instruction make students better spellers, readers, and writers? A meta-analytic review. Reading and Writing, 27(9), 1703-1743.
· Graham, S., Bollinger, A.,Booth Olson, C., D'Aoust, C., MacArthur, C., McCutchen, D., & Olinghouse, N. (2016). Teaching elementary school students to be effective writers: A practice guide (NCEE 2017-4002). Washington, DC: National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance (NCEE), Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education.
· James, K. H., & Engelhardt,L. (2012). The effects of handwriting experience on functional brain development in pre-literate children. Trends in Neuroscience and Education, 1(1), 32-42. doi:10.1016/j.tine.2012.08.001
· Puranik, C., & Lonigan, C.J. (2014). From scribbles to scrabble: Preschool children's developing knowledge of written language. Reading and Writing, 27(2), 267-282. doi:10.1007/s11145-013-9448-9